
MS-Fit | MS-Tag | MS-Seq | MS-Pattern | MS-Homology | MS-Digest | MS-Bridge | MS-NonSpecific | MS-Product | MS-Comp | MS-Isotope | MS-Viewer
This document provides instructions for MS-Viewer.
- Introduction
- Submitting Data to MS-Viewer
- Peak List File Formats
- Results File Formats
- Spectral Identifiers
- Formats for Reporting Peptide Modifications
- Conversion of Result Formats to a Supported Format
- NIST msp and SpectraST sptxt Library Files
- Modification Reporting
- Setting Parameters For Viewing Spectra - MS-Product Parameters
- Setting Parameters for Re-Searching Spectra - MS-Tag Parameters
- Saving Uploaded Results and Parameters
- Running MS-Viewer from the Command Line
- Displaying an MS-Viewer Dataset with a URL
- Script to Convert Mascot CSV File
- Script to Convert Thermo MSF Viewer File
- Script to Convert X!Tandem Tab Delimited File
- Script to Convert MaxQuant msms.txt File
- Script to Convert MS-Amanda File
MS-Viewer is software that allows sharing and visualization of proteomic results created by most search engines. It can be used for sharing results with colleagues, but it is most heavily used for making annotated spectra available for results that are part of a manuscript; a requirement of many proteomic journal publication guidelines. A video tutorial has been produced demonstrating the uploading of data and use of MS-Viewer. More detailed instructions for its use are outlined below.
MS-Viewer requires two types of input files: a peak list file that contains the spectrum information, and a results file that contains the peptide assignments to each spectrum. In some xml results formats, such as PRIDE XML, or database formats, such as Thermo msf files, both of these information types are stored in the same file. If the user has results in one of these formats then the single file can be uploaded as a results file.
The results should be in a single file, but if the dataset corresponds to multiple instrument runs, then multiple peak lists files can be uploaded together in any common archive file format. All of the common peak list formats are supported: mgf, mzData, pkl, dta, mzML, mzXML and ms2. Supported compressed and archive formats include .zip, .7z, .rar, .gz, .z, .bz2, .cmn, .tar, .tgz, .tar.gz, .taz and .tar.z. If your peak list is in a different format and you cannot easily produce one of the formats listed, then contact us () and we will try to assist you.
Unless uploading a supported database or XML format uploaded results files must be in either a tab-delimited text or comma-separated value format. Among the columns in this table there must be one containing peptide sequences (with modifications either within the sequence or as a separate column); one with spectrum identifiers that allow mapping between the results file and the uploaded peak list file/s; and one containing the precursor charge, which is used to determine which charge states should be considered when annotating the spectrum. A fraction column (containing the name of the relevant peak list file) is also required if multiple peak lists are uploaded. An arbitrary number of other columns containing any other information may also be present.
The uploaded results file may be compressed. Currently only multiple msf results files may be uploaded in as an archive file. These must be results from the same search algorithm so that the score columns are compatible.
Scan number, retention time, precursor m/z and spectrum number (order of spectra in peak list file) can be used as spectral identifiers. If retention time is used, make sure the retention time is reported to the same number of significant figures in the peak list file and results file. If precursor m/z is used, be aware that if there are multiple precursors in the peak list file with identical m/z then it may link to the wrong spectrum.
MS-Viewer expects peptide sequences to be in upper case, and if modifications on peptides are listed in the peptide sequence, they should be defined in round parentheses immediately after the modified residue. The only variation on this is that lower case s,t,y and m are interpreted as phosphorylations of ser, thr and tyr or met oxidation, respectively. The modification itself can either be expressed using the PSI-MOD standard nomenclature[11] (listed in Unimod), or it can be reported as a mass (if a mass is reported then this should be exact rather than nominal); e.g. methionine oxidation can be indicated as M(Oxidation) or M(15.995). A modification on the N- or C-terminus is represented by a - before or after the beginning or end residue; e.g. an acetylated protein N-terminal peptide could be listed as Acetyl-MDESTR. The modification can also be described in a different column using the format 'modification@residue_number_in_peptide_sequence'. Using this format it is also possible to represent ambiguous modification site localizations, which can then be displayed and compared in MS-Viewer. Potential ambiguous site localizations should be separated by a |, so if one wanted to represent that a phosphorylation could either be on the sixth or seventh residue in a peptide sequence assignment, then this would be indicated as 'phospho@6|7'. This format also supports neutral loss modifications (where the precursor is modified, but it is assumed that all fragments are unmodified); e.g. Sulfo@Neutral loss would be the most effective way to annotate a sulfated peptide spectrum.
Practically all search engines can produce a tab-delimited text or comma separated value output format. Conversion from one of these formats to a format that MS-Viewer will read can generally be achieved using a simple script or even using Microsoft Excel. This script can be run prior to submission to MS-Viewer, but it is also possible to automatically run scripts during the upload process and this has been enabled for several file formats. The user selects a 'Results File Format' from a list, and for the options other than Protein Prospector Tab Delimited or 'Other', a script will be run in the background to try to convert the relevant format on-the-fly. Example conversion scripts for Mascot CSV files, Thermo MSF viewer output files and X!Tandem Tab Delimited Text files are included in this document as examples. If the user has a file in a different format, and they write a script to enable conversion, then we would encourage them to send us the script (), so we may be able to incorporate this as a new format option for other users.
Below are listed instructions for how to use specific formats. However, there is also a video tutorial that users may find easier to follow than the descriptions below.
To create a Mascot csv results file, in your Mascot results output, specify 'Export Search Results', then click 'Format As':
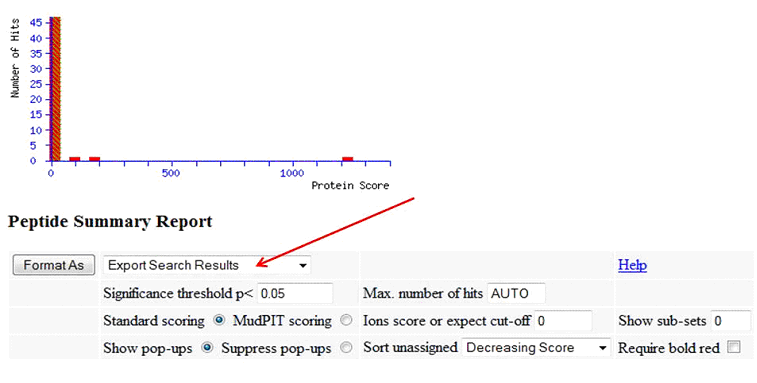
On the following page, as Export format, specify 'CSV':
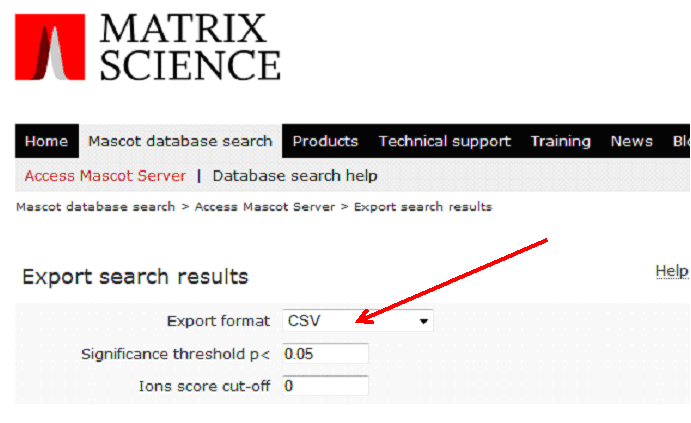
All other parameters can be left as default, then click on 'Export Search Results' at the bottom of the page.
Upon completing your search using X!Tandem you are presented with a protein summary report. To create the tab-delimited text file for MS-Viewer, first click on 'peptide' at the top of the report:
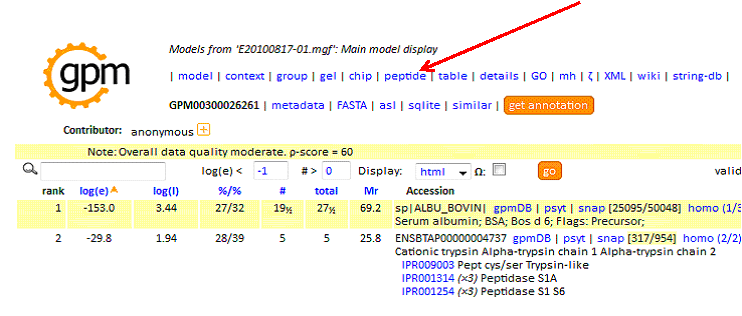
In the peptide report, specify as:'excel', then click 'go' to create the tab-delimited text output:
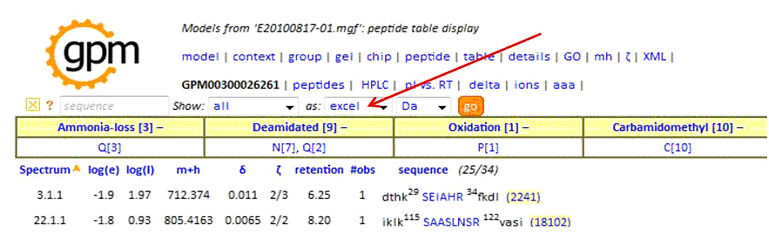
When uploading a MaxQuant data set the Results File Format should be set to MaxQuant. The Peak List File should be an archive file containing the apl files from the combined directory. The Results File should be the msms.txt file from the combined/txt directory. The Instrument Filter option can be used to select either ETD or CID spectra from the msms.txt file based on the contents of the Fragmentation column. If the uploaded report contains both CID and ETD spectra the end user will have to switch between the two by setting the Instrument parameter in the Display and Parameter Settings and then pressing Regenerate Report. If you filter the results in this way then you should only upload the relevant peak file files. During the upload process the apl files are converted to mgf files and the spectra are rearranged by fraction.
The Probability Limit option can be used to set the level at which a site assignment can be considered possible. The default value is 0.05, ie a 5% probability. If you set this to 0 then all potential sites are considered possible. If you set it to 1 then the site chosen is the one designated is the one in the Modified Sequence column of the msms.txt file. The ambiguous site infomation is passed through to the spectral viewer so that the evidence for a given site can be inspected.
If you select the Remove Replicates option then the report will be sorted and filtered to just retain the best spectrum for any given peptide sequence, modifications and precursor charge combination. This is the preferred option if you have a very large data set. Note that to filter the peak list files you also need to keep the Filter Saved Data checkbox checked when saving the data set. If you do this the sizes of the saved peak list files will typically be much smaller and the spectral display will be faster.
If your msms.txt file has a Labelling State column you need to select the appropriate option from the SILAC Labels menu.
Any constant modifications need to be set on the MS Viewer form.
Once the data has been uploaded you might want to remove some columns from the default display and apply some sort and/or filtering options before saving the data set.
The script used to process the msms.txt file is listed here.
Brief instructions:
1). Bring up the MS-Viewer page:
http://msviewer.ucsf.edu/prospector/cgi-bin/msform.cgi?form=msviewer
2). Put the apl files in a zip file and select the zip file using the Peak List File Browse button.
3). Select the msms.txt file using the Results File Browse button.
4). Set the Results File Format option to MaxQuant
5). Set the appropriate SILAC labels from the SILAC labels button. You do not need to upload the summary.txt file.
6). The Instrument Filter option is only relevant if your data set contains both ETD and HCD data.
7). If you want to significantly reduce the size of the report and improve the speed of spectrum display, check the Remove Replicates checkbox. This retains only the best scoring peptide for any combination of peptide sequence, modifications and precursor charge.
8). Set any appropriate Constant Modification. Typically this would be Carbamidomethyl (C).
9). Set an appropriate Frag Tol and Instrument.
10). Press the Upload New Results Green button.
11). Check some of the spectral links. If you are satisfied save the data set. At the top of the report open up the Display and Parameter Setting section. Check Save Settings and then Regenerate Report.
For other file formats the user needs to tell the software which column contains the spectral identifier, peptide sequence, peptide modifications (if not in peptide sequence), precursor charge and peak list file name (if multiple peak list files were uploaded). Most of the parameters required here are self-explanatory. We describe a few of them below:
Num Title Lines: Some results formats have lines at the top that do not contain results (e.g. it may list search parameters used). Specify here how many rows should be ignored.
Num Header Lines: Indicate the number of rows that are column header lines.
For these formats you should be able to just upload the relevant library file as a Results File. The peak lists are included in the library file.
Some search engines report the modifications within the peptide, some as one or more separate columns. Some search engines do not list fixed/constant modifications (as they are assumed to be there). If this is the case, then these modifications need to be selected in the Constant Mods item.
For Prospector results you have the choice whether or not to include constant modifications in the Search Compare results file. If you don't include them in your results file then you need to set them on the Constant Mods item.
For PRIDE XML, pepXML, BiblioSpec and MSFViewer the constant mods are included in the source file and written to the Mods column in the output. Thus you don't need to specify anything on the Constant Mods item.
The script to process Mascot CSV results copies the constant modifications from a header in the original file to a column in the output. Thus you don't need to specify anything on the Constant Mods item.
The scripts to process X!Tandem and MSF Viewer results files have no code to deal with constant mods. Thus whether or not you need to specify anything on the Constant Mods item depends on what is in the original results file you upload.
If you write your own script to process a results file it is up to you how you deal with constant modifications.
The uploaded peak list and results files allow MS-Viewer to match spectra to sequences, but it is necessary to tell MS-Viewer how to annotate the spectra. The user needs to specify what mass tolerance (in absolute or relative mass error) to consider when labeling peaks, and also the fragment ion types to consider. Fragment ions are either specified by the 'Instrument' setting: the ion types considered for each instrument setting are indicated here (link to table in batchtagman.htm) or can be manually specified under 'Ion Types' by deselecting 'Use instrument specific defaults to override ion types below', then selecting the ion types the user wishes annotated. As a default, MS-Viewer will display and annotate all peaks in the peak list file (unprocessed), but it is also possible to threshold the displaying and labeling of the peak list to only the 'n' most intense peaks, or 'n' most intense peaks per m/z 100.
MS-Viewer provides the option for the user to search any individual spectrum of interest using MS-Tag. As well as giving a second opinion on the interpretation of a spectrum if a different search engine was initially used, this also allows the user to search with different search parameters; e.g. searching against a different database or allowing for different modifications. In the 'MS-Tag Parameters' section of the MS-Viewer upload page the user can specify the default parameters to be set when opening a link to search a spectrum. Explanation of all these parameters are in the Batch-Tag manual.
When all of the information described above has been specified, click on 'Upload New Results'. This will upload the data and produce an MS-Viewer output. At this point the uploader should test whether the links work correctly. Clicking on a peptide sequence should display an annotated spectrum, and clicking on the spectrum identifier column (e.g. RT if this was indicated as the spectrum identifier when uploading) should open a link to MS-Tag from File. Expanding the 'Form Settings' at the top of the page allows the user to change any of the parameters that were previously specified, then one can regenerate the report to try to fix any mistakes.
When all parameters are set as desired and the links work, by clicking on 'Save Settings', then when one 'Regenerates Report' instead of re-displaying the results, a permanent url link is created to the results that includes a search key. Note down this Search Key: inputting this on the MS-Viewer home page will take users to the saved results.
As mentioned before, a video tutorial is also available to guide you through many of the steps described in this manual.
For details on options available when viewing an annotated spectrum, please see the MS-Product instruction manual.
If you have lots of data sets to import into MS-Viewer or the data sets are too large to import via the web interface it is possible to run MS-Viewer in a batch mode from the command line using the Perl script automsviewer.pl which is located in the cgi-bin directory. Examples of using the script are given below.
Firstly create a directory structure to hold files to upload to MS-Viewer. Eg on LINUX you could enter the follow commands.
mkdir msvdata cd msvdata mkdir peak mkdir res
Next download the data sets that you want to import into MS-Viewer. As an example we will download some peak lists and the associated results files from the Proteome Exchange.
Firstly download the results files into the res directory.
cd res ftp ftp.pride.ebi.ac.uk
Login as anonymous with no password. Then enter the following commands:
cd 2013/05/PXD000158 prompt mget VK_H*.pep.xml mget VK_D*.pep.xml quit
Next download the peak list files into the peak directory. Note that this step is unnecessary if the data format stores the peak lists in the results files.
cd ../peak ftp ftp.pride.ebi.ac.uk
Login as anonymous with no password. Then enter the following commands:
cd 2013/05/PXD000158 prompt mget VK_H*.ms2 mget VK_D*.ms2 quit
Note that automsviewer.pl deletes the results and peak list files as it processes them so you might want to make a copy of them at this stage.
To connect to the msvdata directory enter the command:
cd ..
The next task is to identify which peak list file corresponds to which results file. If the results files and the corresponding peak list files don't align when sorted alphabetically then you should create two files called say peak.txt and res.txt. The peak.txt file should contain a list of the full paths of the peak list files (one per line) and the res.txt file should contain a list of the full paths of the results files (one per line). The first few lines of an example peak.txt file could be:
/home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D1_1.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D1_2.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D2_1.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D2_2.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D3_1.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D3_2.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D4_1.ms2 /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak/VK_D4_2.ms2
The corresponding lines of the res.txt file would then be:
/home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D1_1.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D1_2.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D2_1.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D2_2.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D3_1.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D3_2.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D4_1.pep.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res/VK_D4_2.pep.xml
It is necessary to create one or more files containing parameters for each time MS-Viewer runs. The parameters that need to be set are those that are different from the default parameters stored in params/msviewer/default.xml.
For example if all data sets require the same parameters you could create a file called params.xml with the following parameters. The .xml file suffix is mandetory.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <parameters> <missed_cleavages>2</missed_cleavages> <msms_parent_mass_tolerance>10</msms_parent_mass_tolerance> <msms_pk_filter>Unprocessed%20MSMS</msms_pk_filter> <column_num_sort_level_1>7</column_num_sort_level_1> <sort_order_direction_1>Descending</sort_order_direction_1> <sort_order_type_1>Numeric</sort_order_type_1> </parameters>
This parameter file ensures that, for example, the resulting MS-Viewer report is sorted by the xcorr score which is in column 7.
If multiple parameter files are required you could create them in a params subdirectory. You would then need a file relating the parameter files with the corresponding peak list and results files. Eg the file could be called params.txt and the first few lines could be:
/home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D1_1.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D1_2.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D2_1.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D2_2.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D3_1.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D3_2.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D4_1.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params/VK_D4_2.xml
It may be necessary to change the permissions on the files so that the user Apache uses can delete them. Eg for Debian you would enter the following commands:
cd .. sudo chown -R www-data msvdata sudo chgrp -R www-data msvdata
To run the automsviewer.pl script first connect to the cgi-bin directory. The command must be run from this directory.
cd /var/lib/prospector/web/cgi-bin
The automsviewer.pl script can be run with either 2 or 3 parameters. The first parameter specifies the parameters, the second the results files and the third the peak list files. The third parameter is optional to cover the case when the peak lists are stored in the results files.
For example assuming there are params.txt, res.txt and peak.txt files a typical command line would be:
sudo -u www-data ./automsviewer.pl /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params.txt /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res.txt /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak.txt
If you want to rely on alphabetic sorting of the results and peak list files then only the corresponding directories need to be specified. In the example below a single parameter file params.xml is also specified.
sudo -u www-data ./automsviewer.pl /home/ppsvr/msvdata/params.xml /home/ppsvr/msvdata/res /home/ppsvr/msvdata/peak
Typical corresponding command lines for Windows could be:
automsviewer.pl G:/msvdata/params.txt G:/msvdata/res.txt G:/msvdata/peak.txt
and:
automsviewer.pl G:/msvdata/params.xml G:/msvdata/res G:/msvdata/peak
| Parameters to Import Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name | Default Value | Valid Values |
| search_name | "" | needs to be set to msviewer |
| report_title | "" | text |
| version | "" | Must be set to current version number or be left blank |
| results_file_format | "" | Protein Prospector Tab Delimited, Protein Prospector Crosslinked Peptides Tab Delimited, PRIDE XML, pepXML, BiblioSpec, Thermo MSF, NIST MSP, Mascot CSV, MaxQuant, Thermo MSF Viewer, X!Tandem Tab Delimited, Other, any other entries added to params/viewer_conv.txt |
| const_mod | None defined | valid text strings formed from the information in params/usermod.txt. Example: Carbamidomethyl (C) |
| Parameters used when importing a dataset into MS-Viewer from the command line | ||
| cl_peak_list_filepath | "" | file path |
| cl_results_filepath | "" | file path |
| Parameters used when uploading data from the MS-Viewer form | ||
| upload_temp_peak_list | "" | file path |
| upload_temp_results | "" | file path |
| Parameters used after a dataset has been imported into MS-Viewer | ||
| peak_list_filepath | "" | file path |
| results_filepath | "" | file path |
| Parameter used to save a data set which has been uploaded by the MS-Viewer form to the repository | ||
| save_params | 0 | 0, 1 |
| search_key | "" | 10 character alphanumeric key |
| Parameters for results_file_format=Other | ||
| column_separator | "" | Tab Delimited, CSV |
| num_title_lines | 0 | positive integer or zero |
| num_header_lines | 0 | positive integer or zero |
| column_num_fraction | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| spectrum_identifier | "" | Protein Prospector RT, Scan Title (Mascot/X!Tandem), Spectrum Number, m/z, Scan Number |
| column_num_scan_id | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_peptide | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_z | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| modifications | "" | Variable Mods In Peptide, All Mods In Peptide, Variable Mods Column, All Mods (1 Column), All Mods (2 Columns) |
| column_num_constant_mod | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_variable_mod | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_all_mod | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| MaxQuant Specific Parameters | ||
| instrument_filter | "" | A string to match the contents from the Fragmentation column in the msms.txt file |
| probability_limit | 0.05 | double value between 0 and 1 |
| remove_replicates | 0 | 0, 1 |
| silac_label | No Labels | No Labels or entry from the file params/mq_silac_options.txt |
| Report Display Parameters (HTML only) | ||
| rows_per_page | 20 | Non-zero positive integer or All |
| page | 1 | Non-zero positive integer |
| Report Filtering Parameters - Note that the column numbers are those after any preprocessing | ||
| column_num_filter_1 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_filter_2 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| filter_type_1 | Equals | Equals, Not Equal To, Greater Than Alphabetic, Greater Than Numeric, Less Than Alphabetic, Less Than Numeric, Contains, Prefix, Suffix |
| filter_type_2 | Equals | Equals, Not Equal To, Greater Than Alphabetic, Greater Than Numeric, Less Than Alphabetic, Less Than Numeric, Contains, Prefix, Suffix |
| filter_value_1 | None Defined | list of text strings |
| filter_value_2 | None Defined | list of text strings |
| Report Sorting Parameters - Note that the column numbers are those after any preprocessing | ||
| column_num_sort_level_1 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_sort_level_2 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_sort_level_3 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| column_num_sort_level_4 | Undefined | Undefined or non-zero positive integer |
| sort_order_direction_1 | Ascending | Ascending or Descending |
| sort_order_direction_2 | Ascending | Ascending or Descending |
| sort_order_direction_3 | Ascending | Ascending or Descending |
| sort_order_direction_4 | Ascending | Ascending or Descending |
| sort_order_type_1 | Alphabetic | Alphabetic or Numeric |
| sort_order_type_2 | Alphabetic | Alphabetic or Numeric |
| sort_order_type_3 | Alphabetic | Alphabetic or Numeric |
| sort_order_type_4 | Alphabetic | Alphabetic or Numeric |
| MS-Product Link Parameters | ||
| parent_mass_convert | monoisotopic | monoisotopic, average |
| fragment_masses_tolerance | 1.0 | double |
| fragment_masses_tolerance_units | Da | Da, %, ppm, mmu |
| instrument_name | "" | valid text strings from params/instrument.txt |
| msms_pk_filter | Max MSMS Pks | Max MSMS Pks, Max MSMS Pks / 100 Da or Unprocessed MSMS |
| msms_max_peaks | "" | integer |
| link_search_type | No Link | valid text strings defined in params/links.txt |
| use_instrument_ion_types | 0 | 0,1 |
| it | None Defined | a,a-H2O,a-NH3,a-H3PO4, b,b-H2O,b-NH3,b+H2O, b-H3PO4,b-SOCH4, y,y-H2O,y-NH3,y-H3PO4,y-SOCH4, MH+,B,c-1,c,c+1,c+2,x,Y,z,z+1,z+2,z+3,n,h,P,S,I,N,C |
| MS-Tag Link Parameters | ||
| database | "" | valid prefixes: Genpept, gen, SwissProt, swp, Owl, owl, UniProt, Ludwignr, NCBInr, nr, dbEST, dbest, pdbEST, pdbest, IPI, ipi, DA, DN, PA, PN, pDA, pDN, Pdefault, Ddefault, pDdefault. User Protein is another possible selection. Multiple databases may be specified. |
| user_protein_sequence | "" | proteins in FASTA format |
| dna_frame_translation | 3 | 6, 3, -3, 1, -1 |
| n_term_aa_limit | "" | Non-zero positive integer or blank |
| species | All | valid text strings from params/taxonomy.txt, params/taxonomy_groups.txt or All |
| output_type | HTML | HTML, XML |
| results_to_file | 0 | 0, 1 |
| output_filename | "" | file name |
| enzyme | Trypsin | valid text strings from params/enzyme.txt or params/enzyme_comb.txt |
| allow_non_specific | at 0 termini | at 0 termini, at 1 termini, at 2 termini, at N termini, at C termini, N termini-1=D |
| missed_cleavages | 1 | integer |
| const_mod2 | None defined | valid text strings formed from the information in params/usermod.txt. Example: Carbamidomethyl (C) |
| msms_prot_low_mass | 1000 | integer |
| msms_prot_high_mass | 100000 | integer |
| msms_full_mw_range | 0 | 0, 1 |
| low_pi | 3.0 | double |
| high_pi | 10.0 | double |
| full_pi_range | 0 | 0, 1 |
| results_from_file | 0 | 0, 1 |
| input_program_name | msfit | msfit, mstag, mspattern, msseq, mshomology |
| input_filename | "" | file name |
| species_remove | 0 | 0, 1 |
| species_names | None Defined | list of text strings |
| accession_nums | None Defined | list of text strings |
| names | None Defined | list of text strings |
| add_accession_numbers | None Defined | list of text strings |
| comment | "" | text |
| msms_max_reported_hits | 50 | integer |
| msms_pk_filter2 | Max MSMS Pks | Max MSMS Pks, Max MSMS Pks / 100 Da or Unprocessed MSMS |
| msms_max_peaks2 | "" | integer |
| expect_calc_method | None | None, Linear Tail Fit |
| msms_mod_AA | None defined | valid text strings formed from the information in params/usermod.txt. Example: Oxidation (M) |
| msms_max_modifications | 1 | integer |
| msms_max_peptide_permutations | "" | Non zero positive integer or blank |
| mod_range_type | Da | Da, m/z |
| mod_start_nominal | 0 | integer |
| mod_end_nominal | 0 | integer |
| mod_defect | 0.0 | double |
| mod_max_z | 1 | Non-zero positive integer |
| mod_comp_ion | None defined | A,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,K,L,M,N,P,Q,R,S,T,V,W,Y |
| mod_n_term_type | Peptide | Protein, Peptide |
| mod_n_term | 0 | 0, 1 |
| mod_c_term_type | Peptide | Protein, Peptide |
| mod_c_term | 0 | 0, 1 |
| mod_uncleaved | 0 | 0, 1 |
| mod_neutral_loss | 0 | 0, 1 |
| link_search_type2 | No Link | valid text strings defined in params/links.txt |
| max_saved_tag_hits | 1000 | Non-zero positive integer |
| link_aa | "" | string of the form C->C where the amino acids on each side of the cross-link are separated by ->. If there are multiple possibilities they should be separated by commas (eg. K,R->K,R). If one possibility is the protein N or C-terminus use this notation: K,Protein N-term->Q. |
| bridge_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_1_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_1 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_1_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_2_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_2 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_2_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_3_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_3 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_3_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_4_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_4 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_4_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_5_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_5 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_5_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| mod_6_label | "" | string |
| aa_modified_6 | "" | An amino acid code or string such as Protein N-term. |
| mod_6_composition | "" | Elemental formula of the form Cx Hy Oz etc where x, y and z are integers. Elements defined in params/elements.txt can be used. |
| msms_search_type | None defined | valid text strings formed from the file params/homology.txt. |
| msms_precursor_charge | Automatic | Automatic or non-zero positive integer |
| parent_mass_convert2 | monoisotopic | monoisotopic, average |
| msms_parent_mass_tolerance | 0.5 | double |
| msms_parent_mass_tolerance_units | Da | Da, %, ppm, mmu |
| msms_parent_mass_systematic_error | 0.0 | double |
| fragment_masses_tolerance2 | 1.0 | double |
| fragment_masses_tolerance_units2 | Da | Da, %, ppm, mmu |
| instrument_name2 | "" | valid text strings from params/instrument.txt |
| uploads_optional | 1 | needs to be set to 1 |
| use_instrument_ion_types2 | 0 | 0,1 |
You can form a URL to display an MS-Viewer dataset such as:
http://prospector2.ucsf.edu/prospector/cgi-bin/mssearch.cgi?search_name=msviewer&report_title=MS-Viewer&rows_per_page=100&search_key=abcdefghij
| Parameters to Retrieve Saved Dataset from MS-Viewer Repository | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name | Default Value | Valid Values |
| search_key | "" | 10 character alphanumeric key |
| rows_per_page | 20 | Non-zero positive integer or All |
| page | 1 | Non-zero positive integer |
| viewer_output_type | "" | HTML, Tab delimited text, Tab delimited text with URL, Viewer files |
| search_name | "" | needs to be set to msviewer |
| report_title | "" | text |
Note you can also use the sorting/filtering option and the MS-Product/MS-Tag link parameters (see above) to override the saved defaults.
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
package Modification; {
sub new {
my $class = shift();
my $self = {};
bless $self, $class;
my ( $v1, $v2, $v3 ) = @_;
$self->{mod} = $v1;
$self->{res} = $v2;
$self->{term} = $v3;
return $self;
}
}
package main; {
my $inFName = $ARGV[0];
my $outFName = $ARGV[1];
open(INFILE,"<$inFName") || die "cannot read filter file";
open(OUTFILE,">$outFName" ) || die "cannot create output file";
my $phase = 0;
my $pepSeqCol = 0;
my $pepModCol = 0;
my %constMod = ();
my %varMod = ();
my $line;
my $lineEnd = "";
while ( $line = <INFILE> ) {
if ( $lineEnd eq "" ) {
if ( $line =~ /\r/ ) {
$lineEnd = "\r\n";
}
else {
$lineEnd = "\n";
}
}
$line =~ s/\s+$//; #remove any white space from end of line
if ( $line =~ /^\"*Fixed modifications\"*/ ) {
$phase = 1;
next;
}
if ( $line =~ /^\"*Variable modifications\"*/ ) {
$phase = 2;
next;
}
if ( $line =~ /^\"*Protein hits\"*/ ) {
$phase = 3;
next;
}
if ( $phase == 1 ) { #define the constant modifications
if ( $line =~ /^(\d+),(.+) \((.+)\),([+-]?(\d+\.\d+|\d+\.|\.\d+))/ ) {
$constMod{$1} = &addModification ( $2, $3 );
}
}
elsif ( $phase == 2 ) { #define the variable modifications
if ( $line =~ /^(\d+),\"*(.+) \((.+)\)\"*,([+-]?(\d+\.\d+|\d+\.|\.\d+))/ ) {
$varMod{$1} = &addModification ( $2, $3 );
}
}
elsif ( $phase == 3 ) { #modify the column headers
if ( $line =~ s/pep_var_mod,pep_var_mod_pos/pep_mod/ ) {
my @headers = &splitCommaNotQuote ( $line );
my $size = @headers;
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $size ; $i++ ) {
if ( $headers [$i] eq "pep_seq" ) {
$pepSeqCol = $i;
}
if ( $headers [$i] eq "pep_mod" ) {
$pepModCol = $i;
last;
}
}
print OUTFILE $line . $lineEnd;
$phase = 4;
}
}
elsif ( $phase == 4 ) {
my @fields = &splitCommaNotQuote ( $line );
my $siz = @fields;
my $mods = &doConstModString ( $fields [$pepSeqCol] ) . &doVariableModString ( $fields [$pepModCol+1] );
chop $mods; #get rid of last semi colon
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $fields [$i];
if ( $i == $pepModCol ) {
$f = $mods;
$i++; #mods are now in a single column
}
if ( $f =~ /,/ ) {
print OUTFILE "\"" . $f . "\"";
}
else {
print OUTFILE $f;
}
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE ",";
}
}
print OUTFILE $lineEnd;
}
}
close INFILE;
close OUTFILE;
sub addModification {
my ( $mod, $res ) = @_;
my $term = "";
if ( $res =~ /C-term(.*)$/ ) {
if ( $1 eq "" ) {
$res = "";
$term = "c";
}
else {
$res = substr $1, 1;
}
}
elsif ( $res =~ /N-term(.*)$/ ) {
if ( $1 eq "" ) {
$res = "";
$term = "n";
}
else {
$res = substr $1, 1;
}
}
return new Modification ( $mod, $res, $term );
}
sub splitCommaNotQuote {
my ( $line ) = @_;
my @fields = ();
while ( $line =~ m/((\")([^\"]*)\"|[^,]*)(,|$)/g ) {
if ( $2 ) {
push( @fields, $3 );
}
else {
push( @fields, $1 );
}
last if ( ! $4 );
}
return @fields;
}
sub doConstModString {
my ( $peptide ) = @_;
my $constModStr = "";
for my $key ( keys %constMod ) {
my $cMod = $constMod{$key};
my $mod = $cMod->{mod};
my $res = $cMod->{res};
my $term = $cMod->{term};
if ( $term eq "n" ) {
$constModStr .= $mod . '@N-term;';
}
elsif ( $term eq "c" ) {
$constModStr .= $mod . '@C-term;';
}
else {
my $i;
my $len = length $res;
for ( $i = 0 ; $i < $len ; $i++ ) {
my $aa = substr $res, $i, 1;
my $idx = 0;
while ( 1 ) {
$idx = index ( $peptide, $aa, $idx );
if ( $idx == -1 ) {
last;
}
$constModStr .= $mod . "@" . ( $idx + 1 ) . ";";
$idx += 1;
}
}
}
}
return $constModStr;
}
sub doVariableModString {
my ( $mask ) = @_;
my $len = length $mask;
my $varModStr = "";
if ( $len > 0 ) {
my $nterm = substr $mask, 0, 1;
if ( $nterm ne "0" ) {
if ( $varMod {$nterm}->{res} eq "" ) {
$varModStr .= $varMod {$nterm}->{mod} . '@N-term;';
}
else {
$varModStr .= $varMod {$nterm}->{mod} . '@1;';
}
}
for ( my $i = 2 ; $i < $len - 2 ; $i++ ) {
my $aa = substr $mask, $i, 1;
if ( $aa ne "0" ) {
$varModStr .= $varMod {$aa}->{mod} . "@" . ( $i - 1 ) . ";";
}
}
my $cterm = substr $mask, $len - 1;
if ( $cterm ne "0" ) {
if ( $varMod {$cterm}->{res} eq "" ) {
$varModStr .= $varMod {$cterm}->{mod} . '@C-term;';
}
else {
$varModStr .= $varMod {$cterm}->{mod} . "@" . ( $len - 4 ) . ";";
}
}
}
return $varModStr;
}
}
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
package main; {
my $inFName = $ARGV[0];
my $outFName = $ARGV[1];
open(INFILE,"<$inFName") || die "cannot read filter file";
open(OUTFILE,">$outFName" ) || die "cannot create output file";
my $phase = 1;
my $pepModCol = 0;
my $line;
my $lineEnd = "";
while ( $line = <INFILE> ) {
if ( $lineEnd eq "" ) {
if ( $line =~ /\r/ ) {
$lineEnd = "\r\n";
}
else {
$lineEnd = "\n";
}
}
$line =~ s/\s+$//; #remove any white space from end of line
if ( $phase == 1 ) { #looking for the header line
my @columns = &splitCommaNotQuote ( $line );
my $siz = @columns;
if ( $line =~ s/Modified Sequence/Modifications/ ) {
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
if ( $columns [$i] eq "Modified Sequence" ) {
$pepModCol = $i;
print OUTFILE $line . $lineEnd;
$phase = 2;
}
}
}
next;
}
if ( $phase == 2 ) {
my @fields = &splitCommaNotQuote ( $line );
my $siz = @fields;
my $mods = &doVariableModString ( $fields [$pepModCol-1], $fields [$pepModCol] );
chop $mods;
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $fields [$i];
if ( $i == $pepModCol ) {
$f = $mods;
}
if ( $f =~ /,/ ) {
print OUTFILE "\"" . $f . "\"";
}
else {
print OUTFILE $f;
}
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE ",";
}
}
print OUTFILE $lineEnd;
}
}
close INFILE;
close OUTFILE;
sub splitCommaNotQuote {
my ( $line ) = @_;
my @fields = ();
while ( $line =~ m/((\")([^\"]*)\"|[^,]*)(,|$)/g ) {
if ( $2 ) {
push( @fields, $3 );
}
else {
push( @fields, $1 );
}
last if ( ! $4 );
}
return @fields;
}
sub doVariableModString {
my ( $pep, $mods ) = @_;
my @parts = split ( /[<>-]+/, $mods );
my @delims = split ( /[^<>-]+/, $mods );
my $off = 0;
my $pepLen = length $pep;
my $nterm;
my $cterm;
my $curMod;
my $varModStr = "";
my $delimIdx = 0;
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < @parts ; $i++ ) {
$delimIdx++;
my $p = $parts[$i];
my $len = length $p;
if ( $off == $pepLen ) {
$cterm .= $p . $delims[$delimIdx];
next;
}
if ( $p eq substr ( $pep, $off, $len ) ) { # this is sequence
$off += $len;
if ( $nterm ne "" ) {
chop $nterm;
if ( $nterm ne "NH2" ) {
$varModStr .= $nterm . '@N-term;';
}
$nterm = "";
}
if ( $curMod ne "" ) {
chop $curMod;
$varModStr .= $curMod . "@" . ( $off - $len ) . ";";
$curMod = "";
}
next;
}
if ( $off == 0 ) {
$nterm .= $p . $delims[$delimIdx];
}
else {
$curMod .= $p . $delims[$delimIdx];
}
}
if ( $cterm ne "COOH" ) {
$varModStr .= $cterm . '@C-term;';
}
return $varModStr;
}
}
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
my $inFName = $ARGV[0];
my $outFName = $ARGV[1];
open(INFILE,"<$inFName") || die "cannot read filter file";
open(OUTFILE,">$outFName" ) || die "cannot create output file";
my $phase = 1;
my $pepModCol = 0;
my $startCol = 0;
my $line;
while ( $line = <INFILE> ) {
my @columns = split ( "\t", $line );
my $siz = @columns;
if ( $columns [0] eq "Spectrum" ) { #this is the header line
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
if ( $columns [$i] eq "start" ) {
$startCol = $i;
}
elsif ( $columns [$i] eq "modifications" ) {
$pepModCol = $i;
last;
}
}
print OUTFILE $line;
$phase = 2;
next;
}
if ( $phase == 2 ) {
my $mod = $columns [$pepModCol];
my $oMod;
if ( $mod !~ /^\s*$/ ) { # If the mod is not blank
my $start = $columns [$startCol];
my @singMods = split ( ",", $mod );
foreach ( @singMods ) {
if ( /\[(\d+)\] ([+-]?(\d+\.\d+|\d+\.|\.\d+))/ ) {
$oMod .= $2;
$oMod .= '@';
$oMod .= $1 - $start + 1;
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
chop $oMod; #delete last semi colon
}
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $columns [$i];
if ( $i == $pepModCol ) {
$f = $oMod;
}
print OUTFILE $f;
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE "\t";
}
}
}
}
close INFILE;
close OUTFILE;
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
package AmbiguousMods; {
my $numSites;
my @sites;
my @sequence;
my $aMods;
sub new {
my ( $probStr, $type, $probLimit ) = @_;
@sites=();
@sequence=();
$aMods = "";
if ( $probStr !~ /^\s*$/ ) { # If the string is not blank
my $offset = 0;
my $totalProb = 0;
while ( $probStr =~ /(\(.+?\))/g ) {
my $prob = $1;
chop $prob; # Strip last character
substr $prob, 0, 1, ""; # Strip first character
$totalProb += $prob;
my $pos = $-[0] - $offset;
if ( $prob > 1.0 - $probLimit ) {
if ( $aMods eq "" ) {
$aMods .= $type;
$aMods .= '@';
}
else {
$aMods .= '&';
}
$aMods .= $pos;
$totalProb -= 1;
}
elsif ( $prob > $probLimit ) {
push ( @sites, $pos );
}
$offset += $+[0] - $-[0];
}
if ( $aMods ne "" ) {
$aMods .= ';';
}
$numSites = int ( $totalProb + 0.5 );
if ( $numSites == 0 ) {
return $aMods;
}
$aMods .= $type;
$aMods .= '@';
if ( $numSites == @sites ) {
foreach my $s (@sites) {
$aMods .= $s;
$aMods .= '&';
}
}
else {
&getNext ( 0 );
}
chop $aMods;
$aMods .= ';';
}
return $aMods;
}
sub getNext {
my ( $level ) = @_;
for ( my $i = $level ; $i < @sites ; $i++ ) {
push ( @sequence, $sites [$i] );
if ( @sequence < $numSites ) {
$level += 1;
&getNext ( $level );
}
else {
for my $s (@sequence) {
$aMods .= $s;
$aMods .= '&';
}
chop $aMods;
$aMods .= '|';
}
pop ( @sequence );
}
}
}
package main; {
my $nargs = @ARGV;
my $filterType;
my $inFName;
my $outFName;
my $probLimit;
my $labels;
$inFName = $ARGV[0];
$outFName = $ARGV[1];
$probLimit = $ARGV[2];
$labels = $ARGV[3];
if ( $nargs > 4 ) {
$filterType = $ARGV[4];
}
$labels = substr $labels, 7;
my %silac;
my @silacAA = ();
my %setSilacAA;
my $silacNTerm = 0;
my $silacZeroLabel = 0;
if ( $labels !~ /^\s*$/ ) { # If the string is not blank
my @silacLabels = split ( "@", $labels );
foreach my $sLabel ( @silacLabels ) {
my $sAA = substr $sLabel, 0, 1;
if ( $sAA ne "n" ) {
if ( !(defined $setSilacAA{$sAA}) ) {
$setSilacAA{$sAA} = 1;
push @silacAA, $sAA;
}
}
else {
$silacNTerm = 1;
}
my $sAANum = substr $sLabel, 0, 2;
my $sNum = substr $sLabel, 1, 1;
if ( $sNum eq "0" ) {
$silacZeroLabel = 1;
}
my $sMod = substr $sLabel, 2;
$sMod .= '@';
$silac{$sAANum} = $sMod;
}
}
my $silacAAs;
foreach ( @silacAA ) {
$silacAAs .= "|" . $_;
}
my $silacRE = "(\\(.+?\\)" . $silacAAs . ")";
my $silacRegExp = qr /$silacRE/;
open(INFILE,"<$inFName") || die "cannot read input file";
open(OUTFILE,">$outFName" ) || die "cannot create output file";
my $phase = 1;
my $modSeqCol = 0;
my $fragCol = 0;
my $silacCol = 0;
my $oxProbCol = 0;
my $phProbCol = 0;
my $caProbCol = 0;
my $coProbCol = 0;
my $acProbCol = 0;
my $d3acProbCol = 0;
my $deProbCol = 0;
my $ggProbCol = 0;
my $laggProbCol = 0;
my $line;
my @columns;
while ( $line = ) {
@columns = split ( "\t", $line );
my $siz = @columns;
my $flag = 0;
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
if ( uc($columns [$i]) eq uc("Raw File") ) {
$flag = 1;
last;
}
}
if ( $flag == 1 ) { #this is the header line
for ( my $j = 0 ; $j < $siz ; $j++ ) {
if ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Modified sequence") ) {
$modSeqCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Oxidation (M) Probabilities") ) {
$oxProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Phospho (STY) Probabilities") ) {
$phProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Carbamidomethyl (C) Probabilities") ) {
$caProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Copy of Lys8 Probabilities") ) {
$coProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Acetyl (K) Probabilities") ) {
$acProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("D3_Acetyl (K) Probabilities") ) {
$d3acProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Deamidation (NQ) Probabilities") ) {
$deProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("GlyGly (K) Probabilities") ) {
$ggProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("LeuArgGlyGly (K) Probabilities") ) {
$laggProbCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Fragmentation") ) {
$fragCol = $j;
}
elsif ( uc($columns [$j]) eq uc("Labeling State") ) {
$silacCol = $j;
last;
}
}
$line =~ s/Modified sequence/Variable mods/i;
if ( $filterType ne "" ) {
$line =~ s/Fragmentation\t//i; #delete Fragmentation column (i - ignore case)
}
print OUTFILE $line;
$phase = 2;
next;
}
if ( $phase == 2 ) { # example _(ac)AAAAAAAGDSDS(ph)WDADAFSVEDPVR_
my $oMod = &getModificationString ( $columns [$modSeqCol], $columns [$silacCol] );
if ( $filterType ne "" ) {
my $fragmentation = $columns [$fragCol];
if ( $fragmentation eq $filterType ) { # only include rows of the correct fragmentation type
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $columns [$i];
if ( $i == $modSeqCol ) {
$f = $oMod;
}
if ( $i != $fragCol ) { # don't output the fragmentation column
print OUTFILE $f;
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE "\t";
}
}
}
}
}
else {
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $columns [$i];
if ( $i == $modSeqCol ) {
$f = $oMod;
}
print OUTFILE $f;
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE "\t";
}
}
}
}
}
close INFILE;
close OUTFILE;
sub getModificationString {
my ( $mod, $label ) = @_;
my $oMod;
my $offset = 0;
my $nterm = 0;
if ( $mod !~ /^\s*$/ ) { # If the mod is not blank
$mod = substr ( $mod, 1 ); # delete first character
chop $mod; # delete last character
while ( $mod =~ /$silacRegExp/g ) { # ? means non-greedy otherwise can match (ac)AAAAAAAGDSDS(ph)
if ( $1 eq "(ac)" ) {
if ( $-[0] == 0 ) {
$oMod .= "Acetyl@";
$oMod .= "N-term";
$oMod .= ';';
$nterm = 1;
}
else {
if ( $probLimit >= 1 ) {
$oMod .= "Acetyl@";
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset;
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
$offset += $+[0] - $-[0];
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(gl)" ) {
if ( $ggProbCol ) {
if ( $probLimit >= 1 ) {
$oMod .= "GlyGly@";
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset;
$oMod .= ';';
}
$offset += $+[0] - $-[0];
}
else {
$oMod .= "Gln->pyro-Glu@" . "N-term";
$offset += $+[0] - $-[0];
$oMod .= ';';
$nterm = 1;
}
}
elsif ( substr ( $1, 0, 1 ) eq "(" ) {
if ( $probLimit >= 1 ) {
if ( $1 eq "(ph)" ) {
$oMod .= "Phospho@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(ca)" ) {
$oMod .= "Carbamidomethyl@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(ox)" ) {
$oMod .= "Oxidation@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(le)" ) {
$oMod .= "LeuArgGlyGly@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(co)" ) {
$oMod .= "Label:13C(6)15N(2)@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(de)" ) {
$oMod .= "Deamidated@";
}
elsif ( $1 eq "(d3)" ) {
$oMod .= "Acetyl:2H(3)";
}
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset;
$oMod .= ';';
}
$offset += $+[0] - $-[0];
}
else {
foreach ( @silacAA ) {
my $aa = $_;
if ( $1 eq $aa ) {
if ( $label eq "0" ) {
if ( $silacZeroLabel ) {
$oMod .= $silac { $aa . "0" };
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset + 1;
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
elsif ( $label eq "1" ) {
$oMod .= $silac { $aa . "1" };
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset + 1;
$oMod .= ';';
}
elsif ( $label eq "2" ) {
$oMod .= $silac { $aa . "2" };
$oMod .= $-[0] - $offset + 1;
$oMod .= ';';
}
last;
}
}
}
}
if ( $silacNTerm && $nterm == 0 ) {
if ( $label eq "0" ) {
if ( $silacZeroLabel ) {
$oMod .= $silac { "n0" };
$oMod .= "N-term";
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
elsif ( $label eq "1" ) {
$oMod .= $silac { "n1" };
$oMod .= "N-term";
$oMod .= ';';
}
elsif ( $label eq "2" ) {
$oMod .= $silac { "n2" };
$oMod .= "N-term";
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
if ( $probLimit < 1.0 ) {
if ( $oxProbCol && length $columns [$oxProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$oxProbCol], "Oxidation", $probLimit );
}
if ( $phProbCol && length $columns [$phProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$phProbCol], "Phospho", $probLimit );
}
if ( $caProbCol && length $columns [$caProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$caProbCol], "Carbamidomethyl", $probLimit );
}
if ( $coProbCol && length $columns [$coProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$coProbCol], "Label:13C(6)15N(2)", $probLimit );
}
if ( $acProbCol && length $columns [$acProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$acProbCol], "Acetyl", $probLimit );
}
if ( $d3acProbCol && length $columns [$d3acProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$d3acProbCol], "Acetyl:2H(3)", $probLimit );
}
if ( $deProbCol && length $columns [$deProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$deProbCol], "Deamidated", $probLimit );
}
if ( $ggProbCol && length $columns [$ggProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$ggProbCol], "GlyGly", $probLimit );
}
if ( $laggProbCol && length $columns [$laggProbCol] ) {
$oMod .= AmbiguousMods::new ( $columns [$laggProbCol], "LeuArgGlyGly", $probLimit );
}
}
chop $oMod;
}
return $oMod;
}
}
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
my $inFName = $ARGV[0];
my $outFName = $ARGV[1];
open(INFILE,"<$inFName") || die "cannot read filter file";
open(OUTFILE,">$outFName" ) || die "cannot create output file";
my $phase = 1;
my $seqCol = 0;
my $pepModCol = 0;
my $fracCol = 0;
my $line;
my $lineEnd = "";
while ( $line = <INFILE> ) {
if ( $lineEnd eq "" ) {
if ( $line =~ /\r/ ) {
$lineEnd = "\r\n";
}
else {
$lineEnd = "\n";
}
}
$line =~ s/\R//g; # Remove the line end
my @columns = split ( "\t", $line );
my $siz = @columns;
if ( $phase == 1 ) {
if ( $columns [0] eq "Scan Number" ) { #this is the header line
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
if ( $columns [$i] eq "Sequence" ) {
$seqCol = $i;
}
elsif ( $columns [$i] eq "Modifications" ) {
$pepModCol = $i;
}
elsif ( $columns [$i] eq "Filename" ) {
$fracCol = $i;
last;
}
}
$phase = 2;
}
print OUTFILE $line . $lineEnd;
next;
}
elsif ( $phase == 2 ) {
my $seq = $columns [$seqCol];
my $oSeq = uc ($seq);
my $mod = $columns [$pepModCol];
my $oMod;
if ( $mod !~ /^\s*$/ ) { # If the mod is not blank
my @singMods = split ( ";", $mod );
foreach ( @singMods ) {
if ( /\w(\d+)\(([^\s\|]+)\|[^s\)]+\)/ ) { # M1(Oxidation|15.994915|variable);M3(Oxidation|15.994915|variable)
$oMod .= $2;
$oMod .= '@';
$oMod .= $1;
$oMod .= ';';
}
}
chop $oMod;
}
my $frac = $columns [$fracCol];
my $oFrac = substr ( $frac, 0, -4 ); #chop off file suffix
for ( my $i = 0 ; $i < $siz ; $i++ ) {
my $f = $columns [$i];
if ( $i == $seqCol ) {
$f = $oSeq;
}
elsif ( $i == $pepModCol ) {
$f = $oMod;
}
elsif ( $i == $fracCol ) {
$f = $oFrac;
}
print OUTFILE $f;
if ( $i != $siz - 1 ) {
print OUTFILE "\t";
}
else {
print OUTFILE $lineEnd;
}
}
}
}
close INFILE;
close OUTFILE;