This document provides instructions for .
- Search Times
- Stopping / Cancelling a Search
- Saving Hits from one Protein Prospector program, searching them with another
- Databases
- Species Filtering
- Intact Protein MW Filtering
- Enzyme specificity / Missed cleavages
- Frame Translation in DNA databases
- General features of links from program output
- Link from the accession number in program output to an annotated remote database entry
- Link from the MS-Digest index number in program output to MS-Digest
- Link from the peptide sequence in program output to MS-Product
- Constant Modifications
- User Specified Amino Acid
- Mass (m/z)
- Mass type
- Charge (z)
- Sample ID (comment)
- Max. Reported Hits
- Max. Hits
- AA Composition Ions
- Absent Amino Acids
- Modified Amino Acids Possibly Present
was originally developed for use with those MALDI-PSD spectra which do not contain a sufficient number of peaks to enable de novo sequence interpretation, but were obtained from peptides whose sequence might be present in a database. The program can also be used with data from MS/MS techniques other than MALDI-PSD simply by selecting fragment-ion types consistent with the technique. MS-Tag can also be used with spectra which contain sufficient information content to enable de novo interpretation; however, a homolog of the peptide must be in the database for a search to be successful.
Checking the boxes next to each ion type allows those ion types to be considered in matching the data to a sequence. Users can either choose to use the default ion types for a particular instrument or a user selected set. Server administrators can modify the default instrument ion types or add new instrument selections. The instrument definition can also include a specification of which amino acids lose water (default S,T,E and D), which lose ammonia (default R,K,N and Q), which are positive charge bearing (default R,H,K and N) and what the maximum internal ion mass is (default 700 Da). Selection of fewer ion types will generally lead to fewer false positives, however ion masses corresponding to ion types not selected or unknown to the program will result in those ion masses NOT being matched. The -SOCH4 and -H3PO4 ion types should only be used in homology mode, and should be selected when the spectrum also contains MH+ - 64 and MH+ - 98 ions respectively. The currently supported ion types are:
| Ion type | Restrictions |
|---|---|
| a, b, y | no restrictions |
| c | not if C term residue of the fragment is P |
| a-NH3, b-NH3, y-NH3 | ion contains an amino acid which loses ammonia |
| b-H2O | ion contains an amino acid which loses water |
| b+H2O | ion contains a positive charge bearing amino acid; only bn-1, bn-2 ( length n) |
| a-H3PO4, b-H3PO4, y-H3PO4 | ion contains phosphorylated S,T |
| b-SOCH4, y-SOCH4 | ion contains oxidized M |
| internal b | < maximum internal mass |
| internal a | < maximum internal mass, internal b present |
| internal b-H2O | < maximum internal mass, internal b present, ion contains an amino acid which loses water |
| internal b-NH3 | < maximum internal mass, ion contains contains an amino acid which loses ammonia |
| N-term ladder | removal of N term residues (y equiv.) |
| C-term ladder | removal of C term residues (b+H2O equiv.) |
While the intact MW of the protein can be specified, MS/MS data is generally of
such high discriminating power that no restriction is necessary. Furthermore, database
entries frequently contain pre and pre-pro proteins, as well as gene fragments.
The tolerances on both the parent ion and fragment ions should be set to be
consistent with the mass accuracy of the instrument used to generate
the data. It is generally a better idea to use units of ppm or % rather than Da.
Fragment mass accuracy is often better at lower mass than at higher mass. For PSD
spectra this is particularly important. If you have +/- 1 Da tolerance
you are more likely to match low mass internal sequences of the wrong nominal mass
thus increasing the likelihood of false-positive hits. Hence setting the
fragment mass accuracy to +/- 1000 ppm prevents this with an "acceptable" trade-off
of allowing looser than appropriate mass accuracy on fragment ions > 1000 Da.
A Fragment-Ion Tag can be obtained from an MS/MS spectrum and consists of 3 attributes:
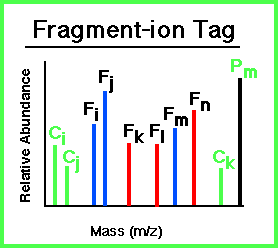
|
|